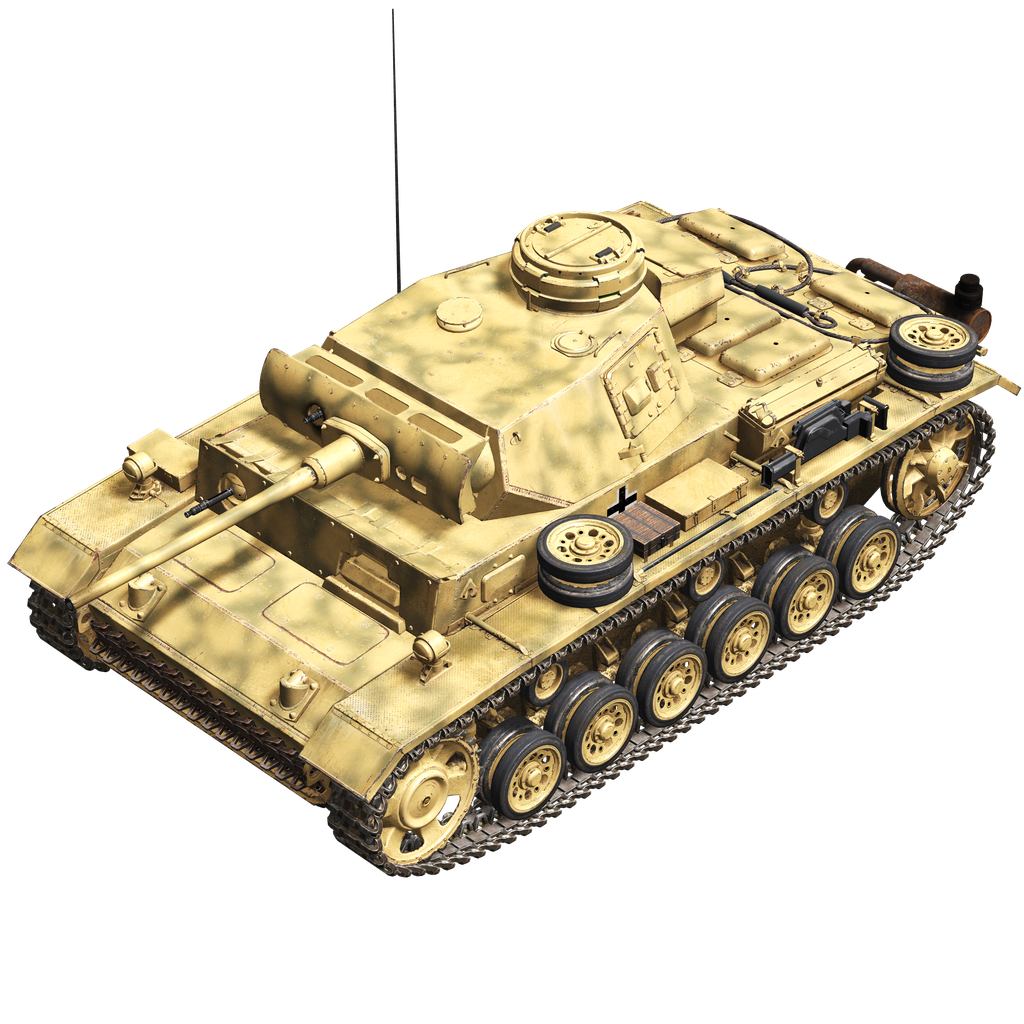
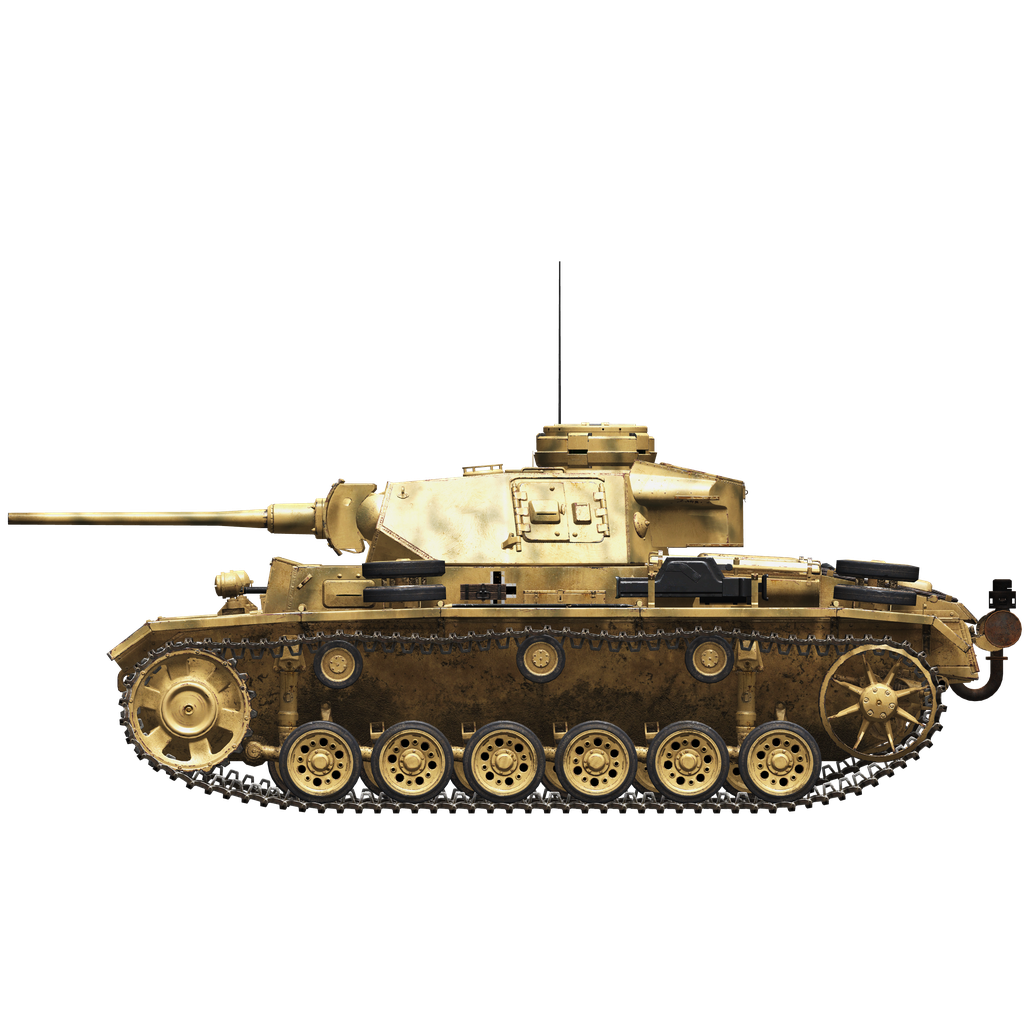
The tank was developed by the designers of the Daimler-Benz company from 1934 to 1937, following a competition announced in 1934 to develop a tank for company commanders, armed with a 37 mm main gun, unlike previous models developed for combat training. It was originally a light (15 ton) tank with bulletproof armor and a chassis with two large diameter road wheels. The tank received the designation Pz.Kpfw.III, and in the Wehrmacht vehicle classification system — Sd.Kfz. 141. During the production process a new, more reliable chassis consisting of two small diameter rollers was introduced. From 1937 to 1938 it was produced in a small series. The first production modification was the Pz.III Ausf E with a chassis with individual torsion bar suspension and increased armor thickness. The production of Pz.III tanks increased continuously and in 1941-1942 they became the most numerous German medium tanks. During the battles with the new Soviet tanks the weakness of the weapons and armor was revealed, so at the end of 1942 modifications with thicker armor and armed with 50 mm cannons were introduced. The last production modification of the tank with a 50 mm cannon was the Pz.Kpfw.III Ausf.M.
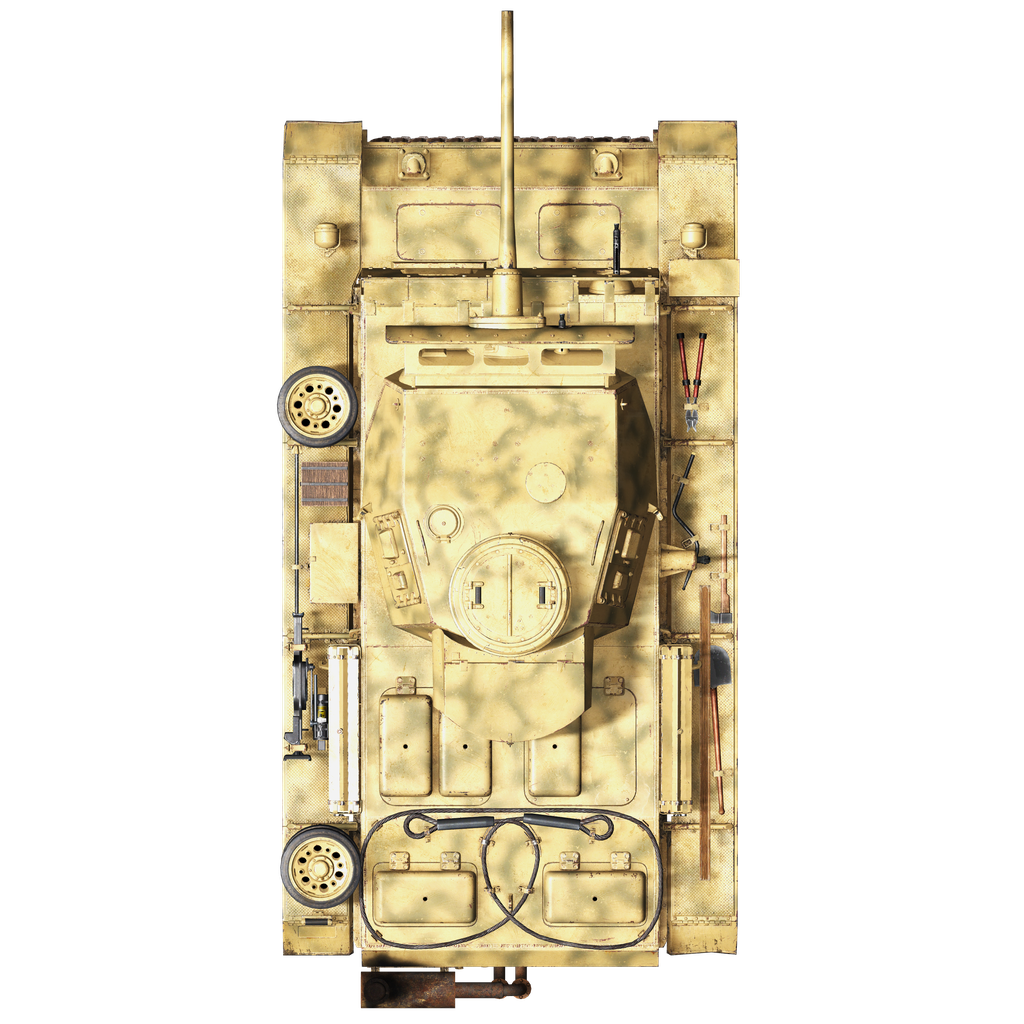
The Pz.III Ausf.M (Sd.Kfz. 141/1) had a classic design with a frontal-mounted transmission. The hull was welded from rolled armor plates. The inner part of the hull was divided into three compartments: control (also known as transmission), fighting, and engine. In contrast to previous modifications, the hatches in the sides of the hull of the Pz.IIIM were removed.
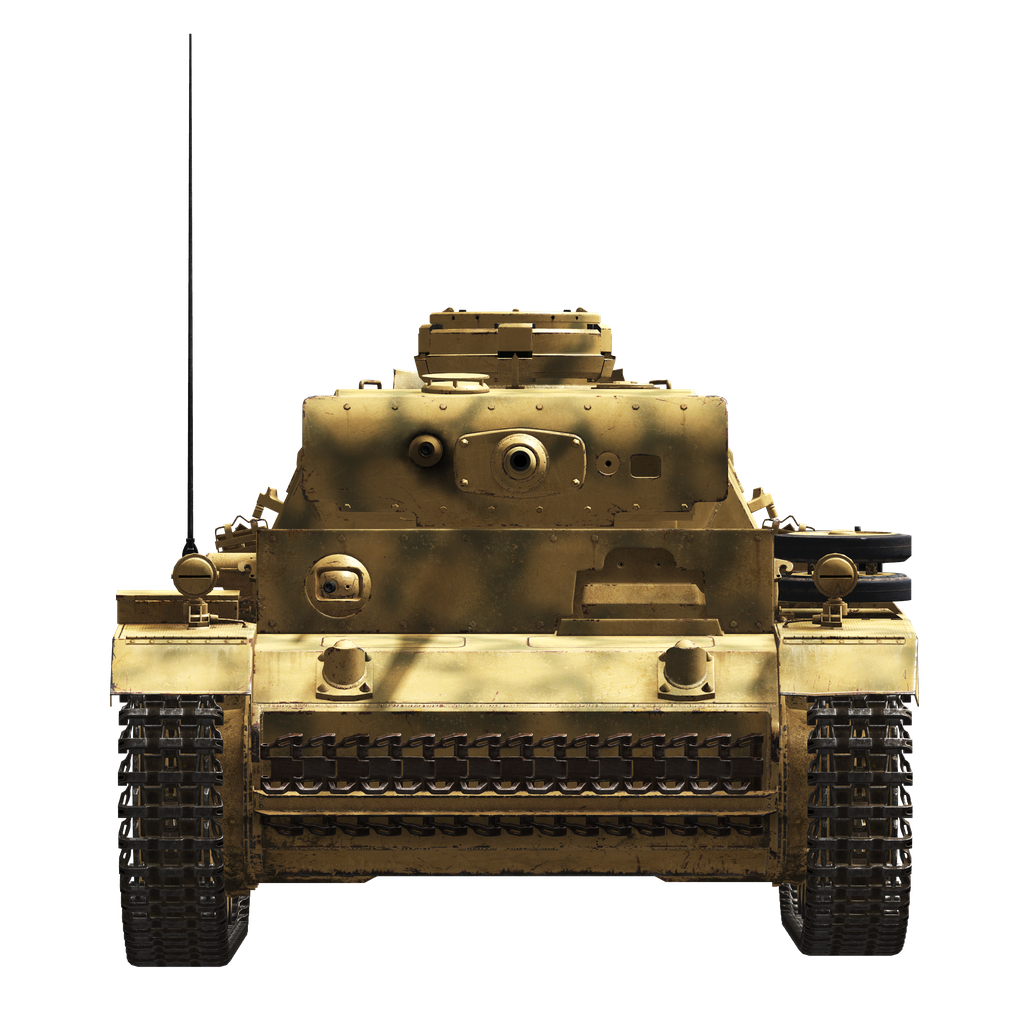
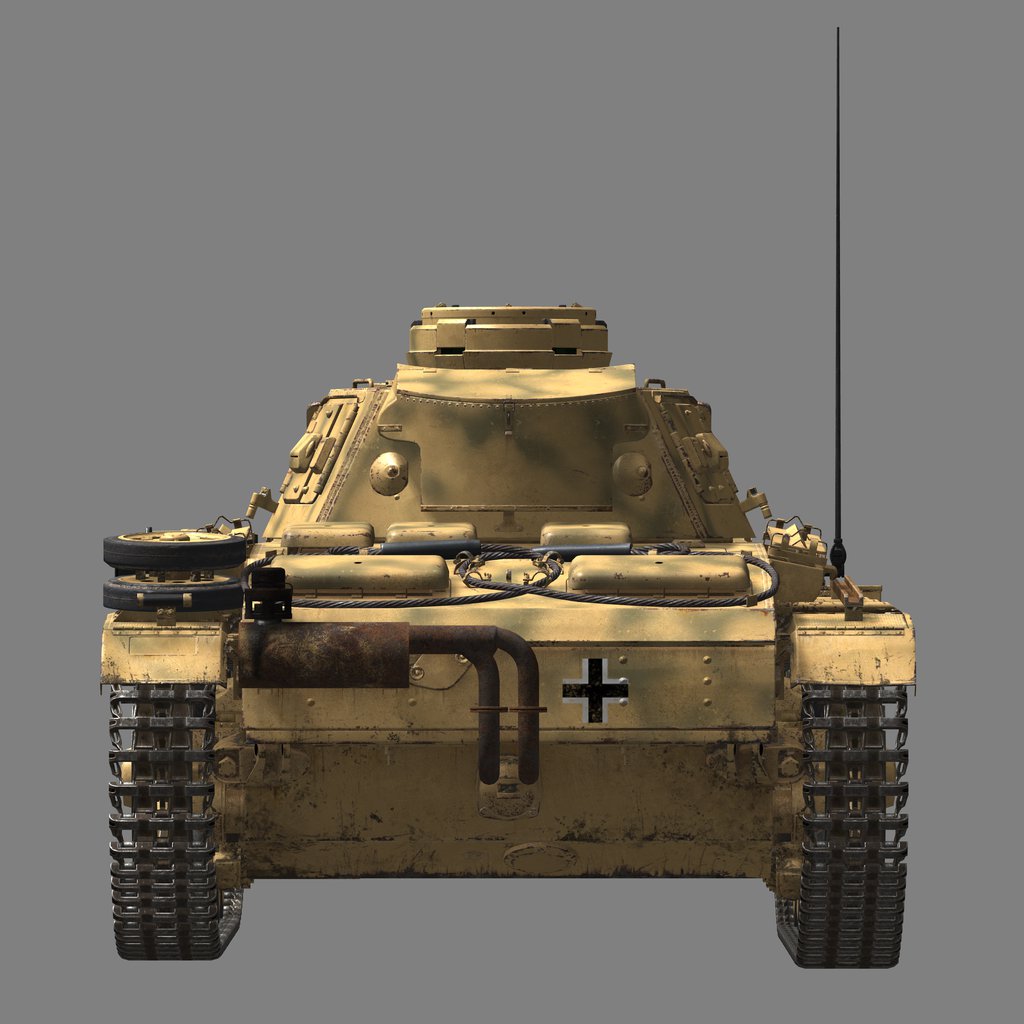
The control compartment was located in the front of the tank. It consisted of seats for the driver and radio operator-machine gunner, control levers, transmission units, control instruments, a radio station, and a machine gun and its ammunition.
The fighting compartment was located in the middle section: there were seats for the tank commander, gunner, and loader and ammunition, increased by eliminating the side hatches. A hexagonal welded turret with a cannon and a coaxial machine gun, a sight and observation devices were installed above the fighting compartment.
The engine compartment was located at the rear of the tank. It contained a Maybach HL120TRM carbureted gasoline engine. The tank's exhaust system was adapted to overcome fords up to 1.3 m deep without preparation.
The armament consisted of a long-barreled 50 mm KwK 39/L60 cannon, two rifle-caliber machine guns and smoke grenade launchers. Types of shells: armor-piercing 5 cm Pzgr. 39 (weight 2.06 kg, initial velocity 835 m/s, armor penetration 68 mm at a distance of 500 m), sub-caliber 5 cm Pzgr. 40 (925 g, 1180 m/s, armor penetration 175 mm) and high-explosive fragmentation 5 cm Sprgr. 38 (1.81 kg, 550 m/s).
A total of 250 Pz.IIIs were produced between November 1942 and February 1943, and the last time they were used en masse was during Operation Citadel. At the beginning of this operation, the tank and motorized divisions of the Wehrmacht and SS troops had 528 tanks with 50 mm long-barreled guns, including the Pz.IIIM modification. According to German data, up to 385 "troikas" were lost in the battle, and by the end of 1943, due to the cessation of production, the number of Pz.IIIs in first-line units decreased sharply — a significant number of tanks of this type were transferred to various training and reserve units. They served in minor theaters of war like Italy and the Balkans. By March 1945 only 164 Pz.IIIs of various modifications remained in Wehrmacht combat units.
Used sources:
1. M. Baryatinsky “Panzer III: Steel symbol of the blitzkrieg” 2008
2. A. Lobanov “Hitler’s Tank Forces” 2010
3. W.Spielberger. "Der Panzerkampfwagen III und seine Abarten" 1994
Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf.M was similar to the previous modification Ausf.L. Some internal, chassis, engine compartment and other elements were altered based on the service experience.
The most apparent visual difference was the addition of side armor plates, "Schürzen", which were attached to the hull and turret sides. They were added mainly to protect the tank from massed AT rifle fire which was dangerous for thinner armored sides. Not being able to stop an AP bullet, this additional armor destabilized it or caused its fragmentation before it could hit the main armored hull.
It should be noted that the front armor was relatively thick thanks to the additional armor plates mounted there in spaced configuration.
The tank could be equipped with six mortars mounted on the turret and designed to shoot smoke grenades at a distance of about 80 meters.
APCR rounds fired from 50 mm KwK 39/L60 gun could penetrate the armor of Soviet medium and heavy tanks at a distance up to 500 m, while regular APHE rounds could be used against sides of medium tanks up to 1 km.
Total 517 tanks of this modification were produced since September 1942 until February 1943.
Unladen weight: 22700 kg.
Length: 6.3 m.
Width: 3.22 m.
Height: 2.5 m.
Clearance: 385 mm.
Engine: Maybach HL 120TRM, petrol.
Maximum power: 300 HP at 3000 RPM.
Maximum RPM: 3000 RPM.
6 speed gearbox.
Maximum road speed:
1-st: 4.8 kph.
2-nd: 9.2 kph.
3-rd: 15.5 kph.
4-th: 23.5 kph.
5-th: 33.2 kph.
6-th: 42.8 kph.
Reverse: 5.9 kph.
Maximum offroad speed: 18 kph.
Fluids:
Internal fuel tanks capacity: 320 l.
Engine oil system capacity: 25 l.
Summer engine coolant: 100 l. of 40% glysantin
Winter engine coolant: 100 l. of 60% glysantin
Endurance range: 155 km.
Maximum oil consumption: 2 l/h.
Hull armor:
Upper front: 50 mm + 20 mm rolled armor.
Middle front: 25 mm rolled armor.
Lower front: 50 mm rolled armor.
Bottom front: 30 mm rolled armor.
Sides: 30 mm rolled armor.
Upper rear: 30 mm rolled armor.
Middle rear: 50 mm rolled armor.
Lower rear: 30 mm rolled armor.
Roof front: 10 mm rolled armor.
Roof back: 15 mm cast armor.
Bottom: 15 mm rolled armor.
Turret armor:
Front: 37..50 mm rolled armor.
Sides: 30 mm rolled armor.
Rear: 30 mm rolled armor.
Roof: 18 mm rolled armor.
Cupola: 50 mm cast armor.
Gun mantlet: 50 mm cast + 20 mm rolled armor.
Additional armor sheets:
5 mm rolled armor for additional protection against AT rifles.
Main gun: rifled, 5 cm KwK 39 L/60.
Barrel length: 56.5.
Elevation: +20°..-8°.
Ammo: up to 84 rounds.
Usable rate of fire: 15 rounds per minute.
Turret drive: mechanical, 33 seconds per rotation.
Gun ammunition:
5 cm Pzgr. 39 armor piercing high explosive (APHE): 2.06 kg, 835 m/s, 68 mm at 500 m.
5 cm Pzgr. 40 armor piercing composite rigid (APCR): 0.925 kg, 1180 m/s, 175 mm point blank.
5 cm Sprgr. 38 high explosive (HE): 1.81 kg, 550 m/s, 175 g. explosives.
Machineguns: 7.92 mm Maschinengewehr 34.
Bullet mass: 11.5 g.
Muzzle velocity: 855 m/s.
Armour pentration at 100 m: 11 mm.
Rate of fire: 900 rounds per minute.
Coaxial: 33 belts, 150 rounds per belt (4950 rounds).
Bow: +-15°/+20°..-10°, 12 belts, 150 rounds per belt (1800 rounds).
Gunsights:
Tzf 5e gunner scope-sight, field of view 25°.
Backup open-type sight with closable port.
KZF 2 machinegunner scope-sight, field of view 18°.
Radio equipment:
VHF Fu 5 transceiver with additional Fu 2 receiver.
3 intercom terminals.